This TETRA project, supported by the Innovation & Entrepreneurship Agency will apply the knowledge acquired around Generative AI to the creative industry.
Situation
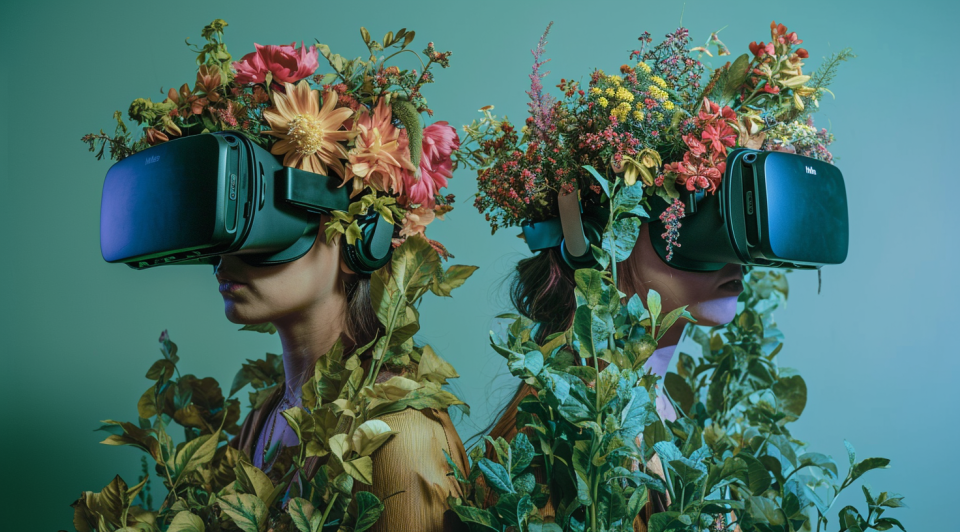
With the rise of Generative AI, we are on the eve of a revolution in the creative industries. Generative AI includes algorithms that can be used to create new content, such as audio, code, text, images and video (McKinsey, 2023). The latest innovations in this field are happening through diffusion models: recent examples include text-to-image applications such as DALL-E 2, Midjourney and Stable Diffusion. These applications, which generate images from a textual briefing (the text prompt), are evolving rapidly in terms of quality and application possibilities. The Creative AI project aims to optimally prepare Flemish SMEs in the creative industry for this revolution.
In recent months, text-to-image algorithms are causing a shockwave in the creative sector. For the visual design sector, the advent of Generative AI is as profound as the introduction of Photoshop and 3D animation. However, the successive evolutions and plethora of AI tools make it difficult for SMEs to grasp what the technology is capable of and to keep their finger on the pulse. Moreover, text-to-image applications are primarily consumer-facing as Proof of Concept (POC). Flemish SMEs still experience barriers to implementing the technology in a professional context. This emerged from the field survey of 25 design agencies for AI-Driven Design (PWO, 2020-2022) and was confirmed during discussions with the guidance group (+60 companies). To meet these needs, creative, technological and user research profiles of three research groups of AP Hogeschool Antwerp are working together multidisciplinary: Immersive Lab; Media, Design and IT and MAXlab (Royal Academy of Fine Arts Antwerp), which combine their expertise around AI, audiovisual and immersive production and user research.
This project aligns with the central objective of the Flemish AI Policy Plan (2019) on the one hand by focusing on the implementation of Generative AI applications in the Flemish creative industry and on the other hand by responding to urgent training needs of the labor market and formulating policy recommendations around legal, ethical and deontological aspects of AI.
Overall objective
The Creative AI project aims to provide useful tools to the creative industries: design, advertising and marketing, media and video and eXtended Reality (XR). Specifically, we are responding to the following needs that we identified through various field consultations (in the Deep Design Dreams, AI-Driven Design and Creative AI projects):
- Radar function and value-added AI tools (WP 1): Companies are looking beyond the hype and want to know which AI tools are already deployable in workflows. Due to rapid technological evolutions and lack of R&D department, they cannot test these diverse tools themselves and assess the added value.
- Technological and creative barriers (WP 2): Professionals do not achieve the desired results with the available tools and cannot iteratively work toward professional results through focused monitoring. Creative AI addresses these and other creative as well as technological thresholds.
- Legal, ethical and deontological questions (WP 3): Companies have legal questions around intellectual property. Media players have ethical and deontological questions around news.
- Identifying training needs (WP 4): Without prior knowledge it is difficult to achieve professional results through prompting, therefore new skills and training are needed.
Specific goals
- Creative Industry Radar (WP 1): Detect, align with industry needs, test and evaluate new Generative AI applications.
- Lowering Creative and Technological Barriers (WP 2): Develop inspiring Proof of Concepts (POCs) and prototypes around 4 themes (see Figure 1) that connect to the daily workings of creative professionals, such as ideation and workflow optimization. We will open the "black box" and adapt existing AI tools for professional use.
- Policy recommendations regarding legal, ethical, deontological questions (WP 3): From desk research, interviews and user research, formulate recommendations for policy makers.
- Training package development (WP 4): Infosessions (broad audience), workshops (general or/and thematic), blueprints, teaching materials (tutorials, powerpoints, frequently asked questions) based on an inspiration guide for generating original imagery tailored to the user's intentions.
Success Indicators
- KPI 1: Specifically, we want to reach 40 companies and non-profit organizations (after 1 y) and 80 (after 2 y), who indicate that they will apply the knowledge of the Tetra project.
- KPI 2: To illustrate the potential of AI tools, we are developing 10 POCs (after 1y) and 4 prototypes (after 2y).
- KPI 3: We aspire to engage 340 (after 1y) and 706 students (after 2y) passively and actively through guest lectures, workshops, undergraduate theses, student projects and internships.
- KPI 4: We aim to disseminate knowledge through 5 publications (after 1y) and 10 publications (after 2y): such as lectures at conferences, publications in newsletters/professional journals and academic publications.
Expected results and impact
- Achieve sustainable economic impact among over 200 creative sector companies (2y after project) that can work more efficiently, thanks to better knowledge and skills on Generative AI and adapted AI tools in the creative industry.
- Formulate policy recommendations around legal, ethical and deontological aspects of AI.
- Integration of project results in relevant courses (undergraduate and professional).
More information? Mail to immersivelab@ap.be (Jeroen Cluckers en dr Silvia Van Aken, projectverantwoordelijken).